March 29, 2024
Combating Workforce Shortages in Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Look
The American workforce has undergone significant upheavals in recent years, especially regarding the workforce shortages in manufacturing. Termed as ‘The Great Resignation,’ a vast number of workers across various industries opted to leave their jobs in pursuit of improved work-life balance, better compensation, or more favorable company cultures. However, this phenomenon has evolved into what we now recognize as ‘The Great Reshuffle,’ wherein hiring rates have consistently surpassed quit rates, indicating a broader realignment in the labor market.
In the manufacturing sector, the pandemic dealt a severe blow, resulting in the loss of approximately 1.4 million jobs during its onset. Despite strides towards recovery, substantial job vacancies persist, with 616,000 openings remaining unfilled in the manufacturing industry as of August 2023. Conversely, the construction industry faces a labor surplus, highlighting the complexity of labor dynamics across different sectors.
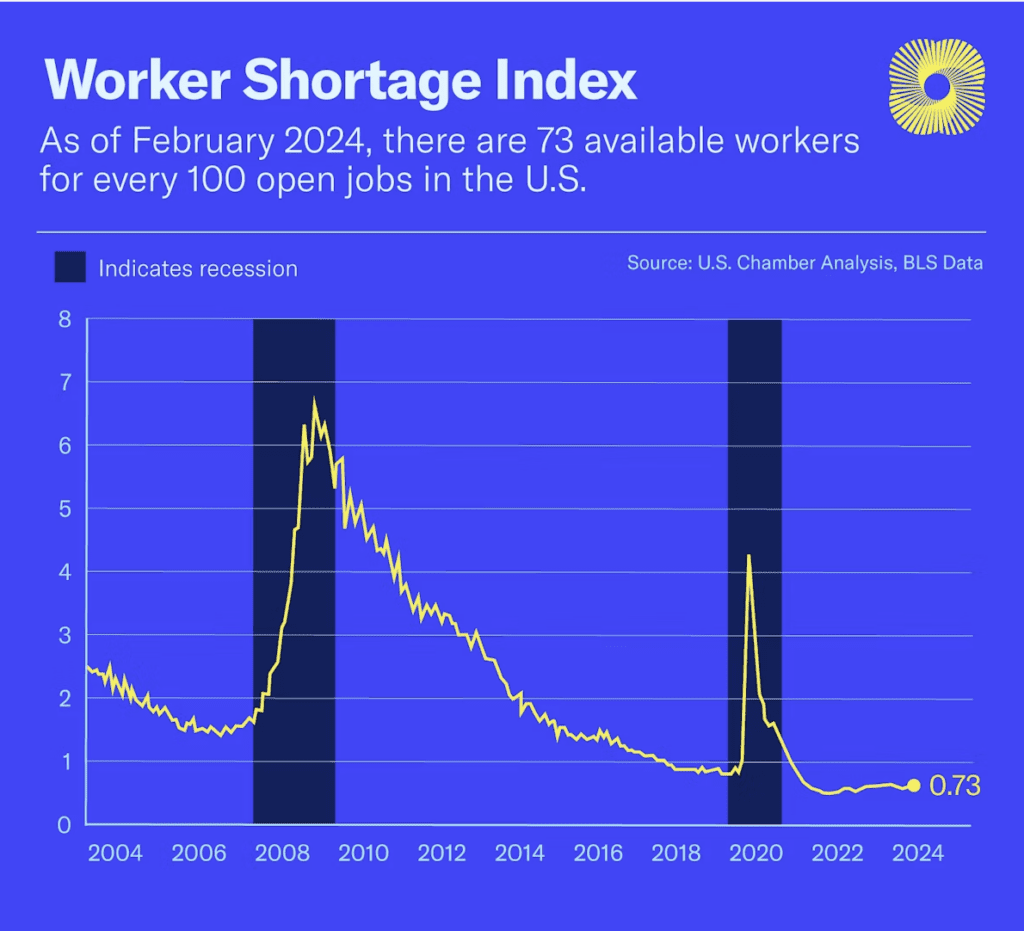
This workforce shortage extends beyond manufacturing, impacting nearly every industry in every state. The gap between job openings and available workers remains wide, with various factors contributing to this imbalance. The pandemic induced early retirements, reduced immigration, and government support programs altered workforce dynamics, leaving the nation grappling with a significant worker deficit.
Initiatives to address this crisis have seen businesses deploying innovative strategies to attract and retain talent. Measures such as expanding childcare access, offering innovative benefits, second-chance hiring, and upskilling and reskilling programs have been advocated to bolster hiring pools and enhance workforce capabilities.
Strategies for Mitigating Workforce Shortages
1. Enhanced Hiring Practices: Businesses can adopt innovative hiring practices to attract and retain talent. Strategies such as second-chance hiring, upskilling, and reskilling programs can expand the pool of qualified candidates.
2. Promoting Industry Appeal: Efforts to enhance the appeal of manufacturing careers can help address workforce shortages. Highlighting the industry’s technological advancements, competitive salaries, and opportunities for career advancement can attract new talent.
3. Leveraging Nearshoring: Nearshoring to countries like Mexico presents an opportunity to bolster the manufacturing workforce while mitigating supply chain vulnerabilities. The advantages of localization, free trade agreements, and lower geopolitical risks make nearshoring an attractive option for manufacturers.
Navigating the Changing Labor Landscape
1. Resilience and Adaptability: Despite challenges, the manufacturing industry has demonstrated resilience and adaptability in response to workforce shortages. Businesses have pivoted their hiring strategies and implemented innovative solutions to address evolving labor market dynamics.
2. Collaborative Efforts: Collaboration between businesses, government agencies, and educational institutions is essential in fostering a skilled manufacturing workforce. By working together, stakeholders can develop targeted initiatives to address workforce challenges and drive industry growth.
3. Strategic Foresight: Embracing strategic foresight in sourcing decisions is crucial in navigating workforce shortages. Considerations such as geopolitical risk analysis can inform sourcing strategies and mitigate potential disruptions in the supply chain.
As the labor market continues to evolve, collaborative efforts between businesses, government agencies, and educational institutions will be crucial in fostering resilience, driving innovation, and nurturing a skilled workforce capable of meeting the demands of the future. By embracing adaptability, innovation, and collaboration, the manufacturing industry can navigate the current workforce shortage landscape and emerge stronger in the years ahead.
Data taken from:
- U.S. Chamber of Commerce

